Basic Design
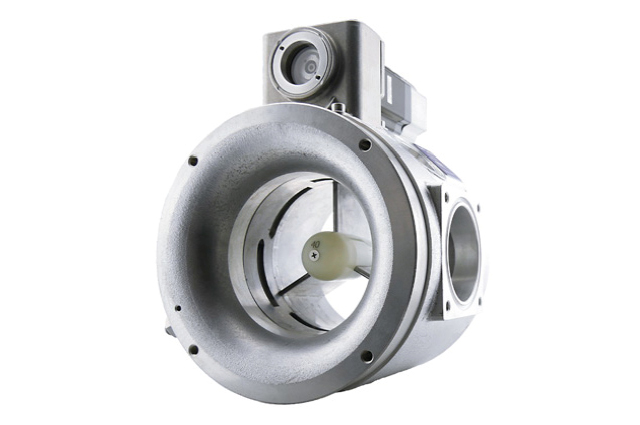
The main task of a gas mixer is to mix the fuel (gas) and air in such a way that optimum combustion takes place in the gas engine. High efficiency and low emissions, in accordance with current regulations, are the decisive parameters for optimization.
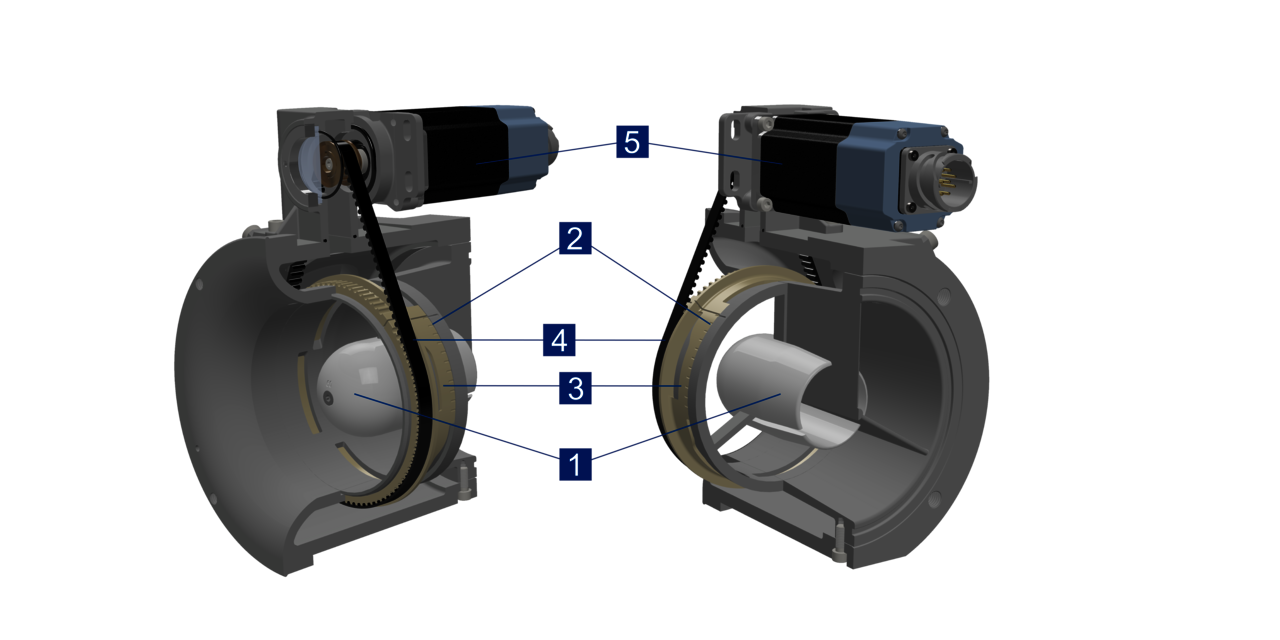
In the VariFuel2, air and gas are mixed according to the Venturi principle. The air is sucked through the air intake into the Venturi nozzle by the suction vacuum of the engine. Due to the Venturi principle, a vacuum is created at the narrowest point, which sucks the gas through the gas inlet. In this way, gas and air are mixed and released at the mixture outlet. Various mixer sizes and flow bodies (1) in the Venturi nozzle allow different volumetric flows to be achieved.
Regulation of the Air/Fuel Mixture
The fuel (gas) is guided into the nozzle via the adjustable openings (2) in a fuel ring (3). The openings of the fuel ring are adjusted by a drive belt (4) via a stepper motor. The stepper motor (5) can be controlled by the VariStep3 stepper motor driver, which can process the signals of a master control. In addition, the VariFuel2 air/gas mixers are equipped with a port for an air pressure gauge and a connection for the pulse line of a zero pressure regulator.
VariFuel3 air/gas mixers are specially designed for use with multiple gas-powered gas-otto-engines and are based on the general operating principle of the VariFuel2 series. The geometry of the built-in fuel ring, adapted to the application, ensures improved engine starting behavior and control of the air-fuel ratio on multiple gas engine applications.
Downloads
MOTORTECH GmbH | Hunaeusstrasse 5 | 29227 Celle, Germany | Phone: +49 5141 9399 0 | Send Email